Rearranging Sediment: A Scale Shifting Pursuit of Pleasure
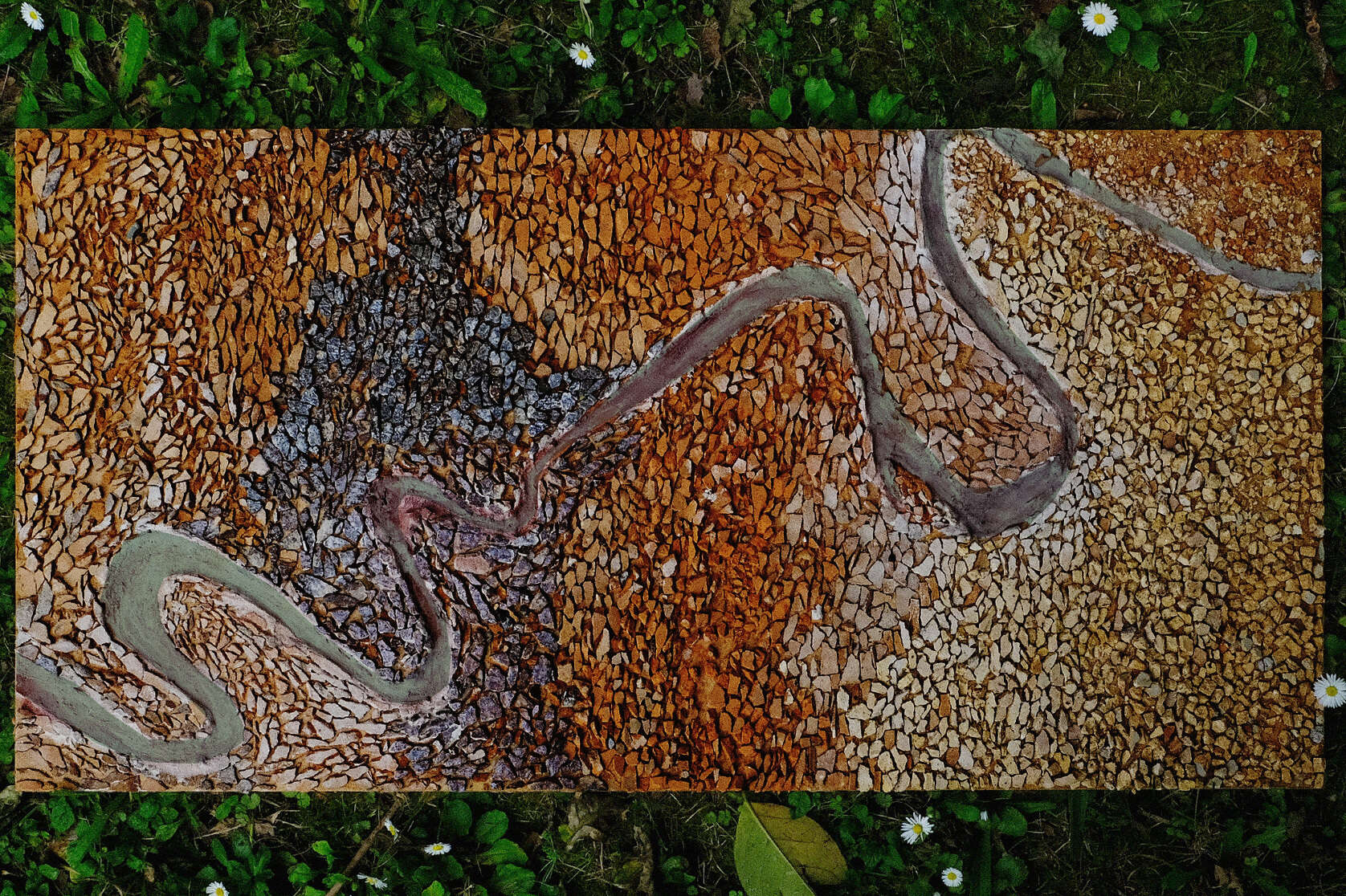

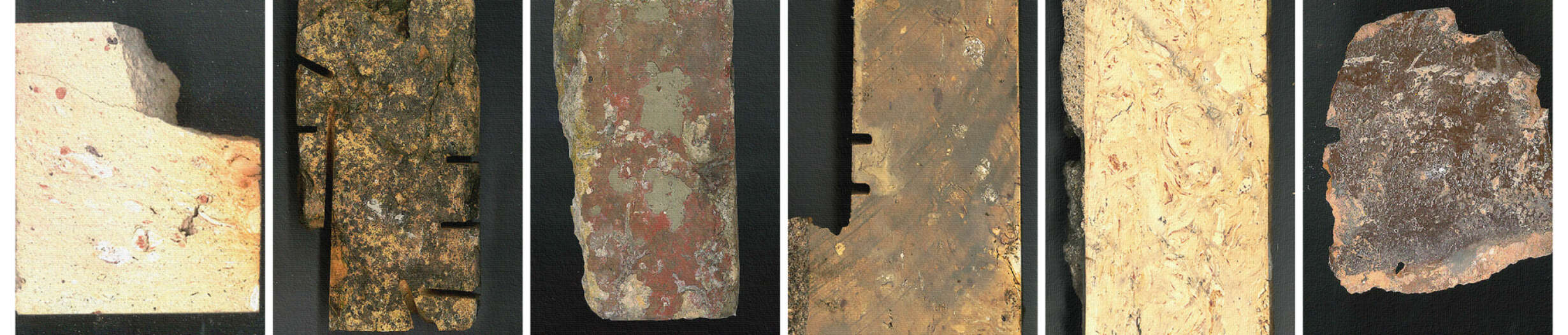
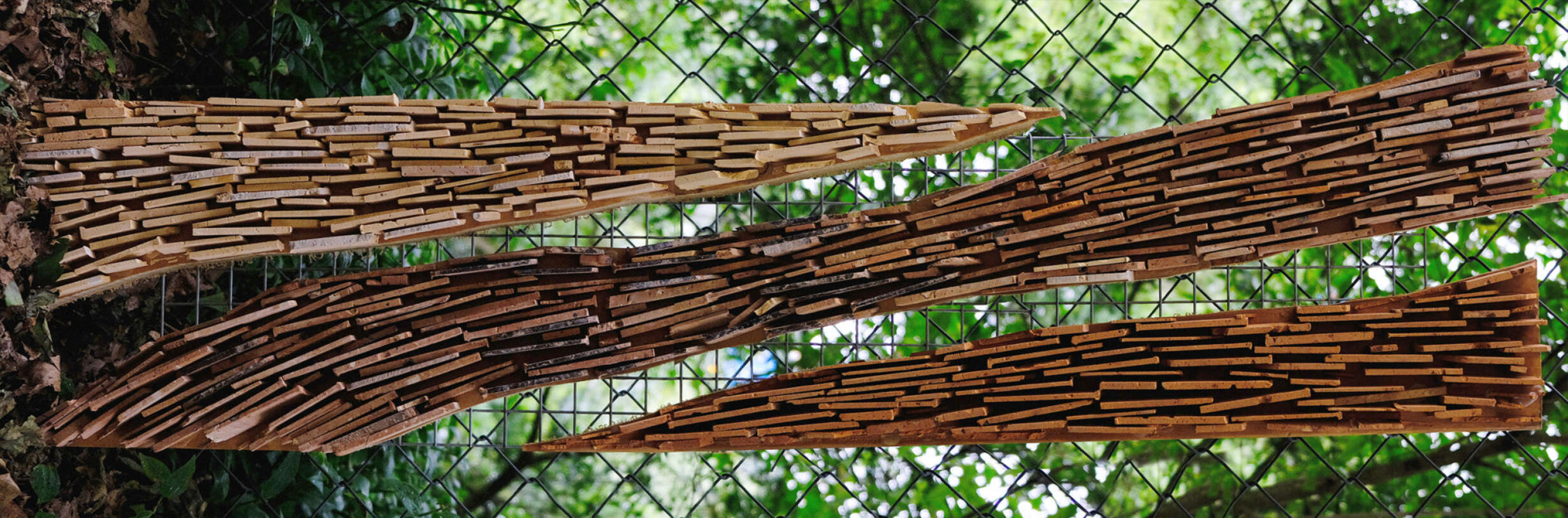
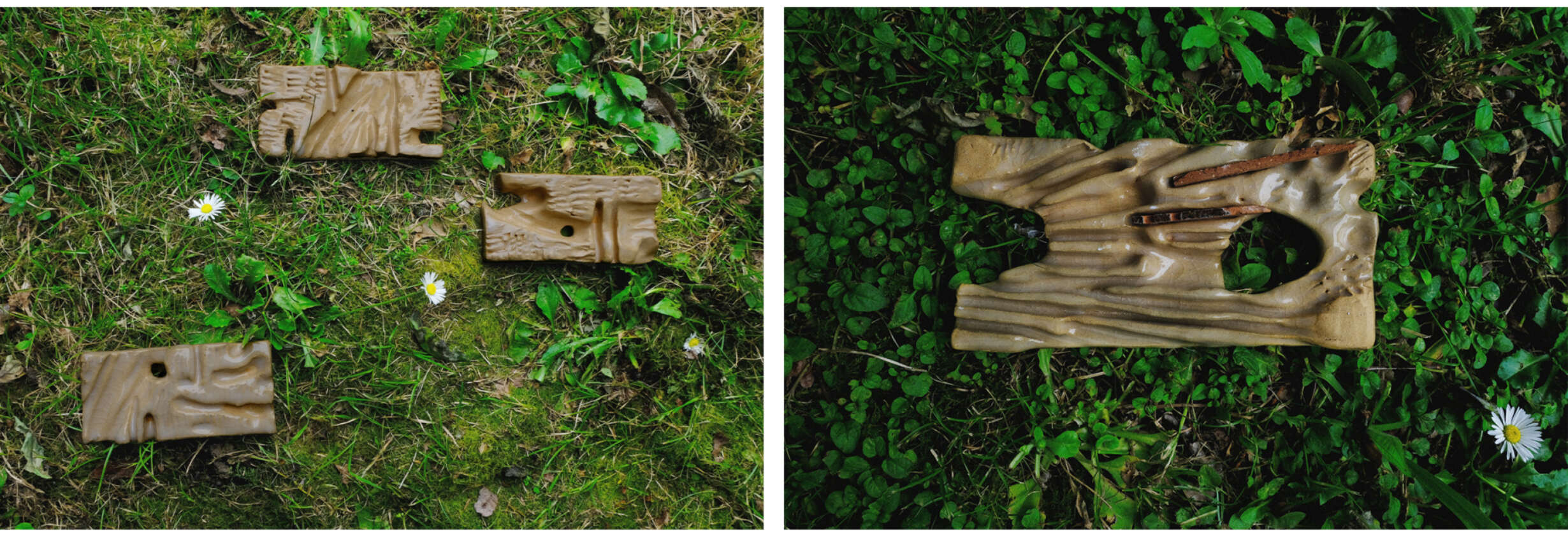
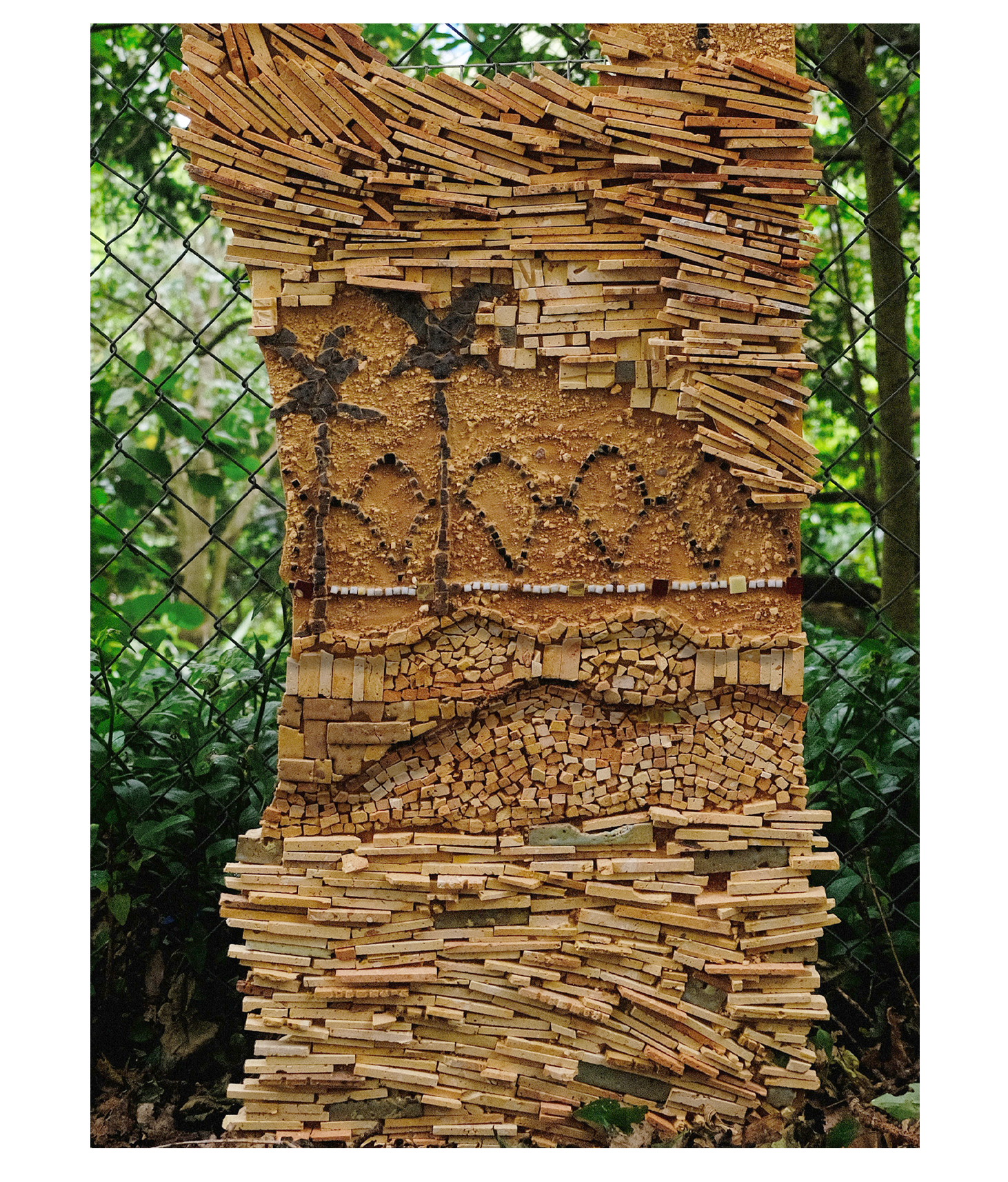
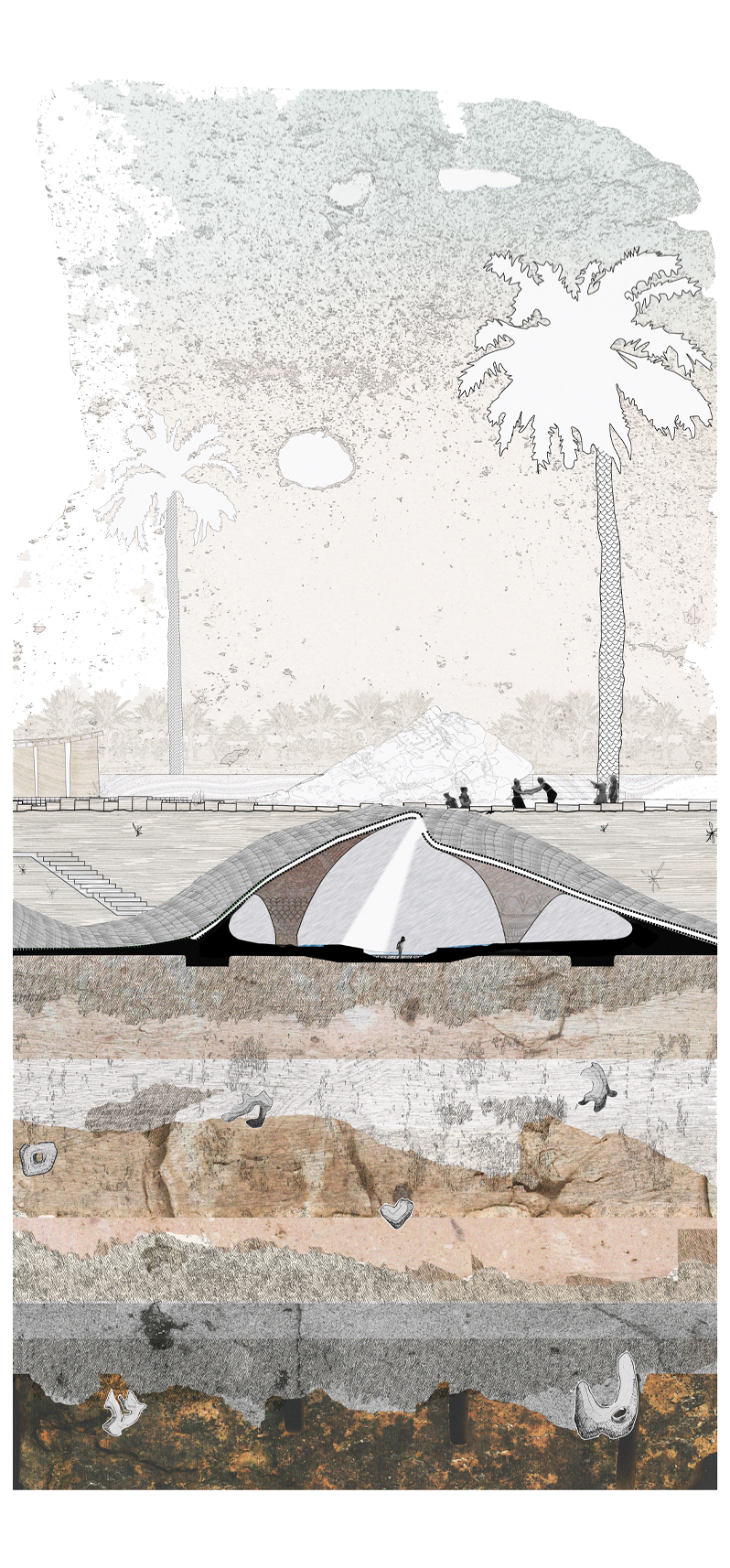
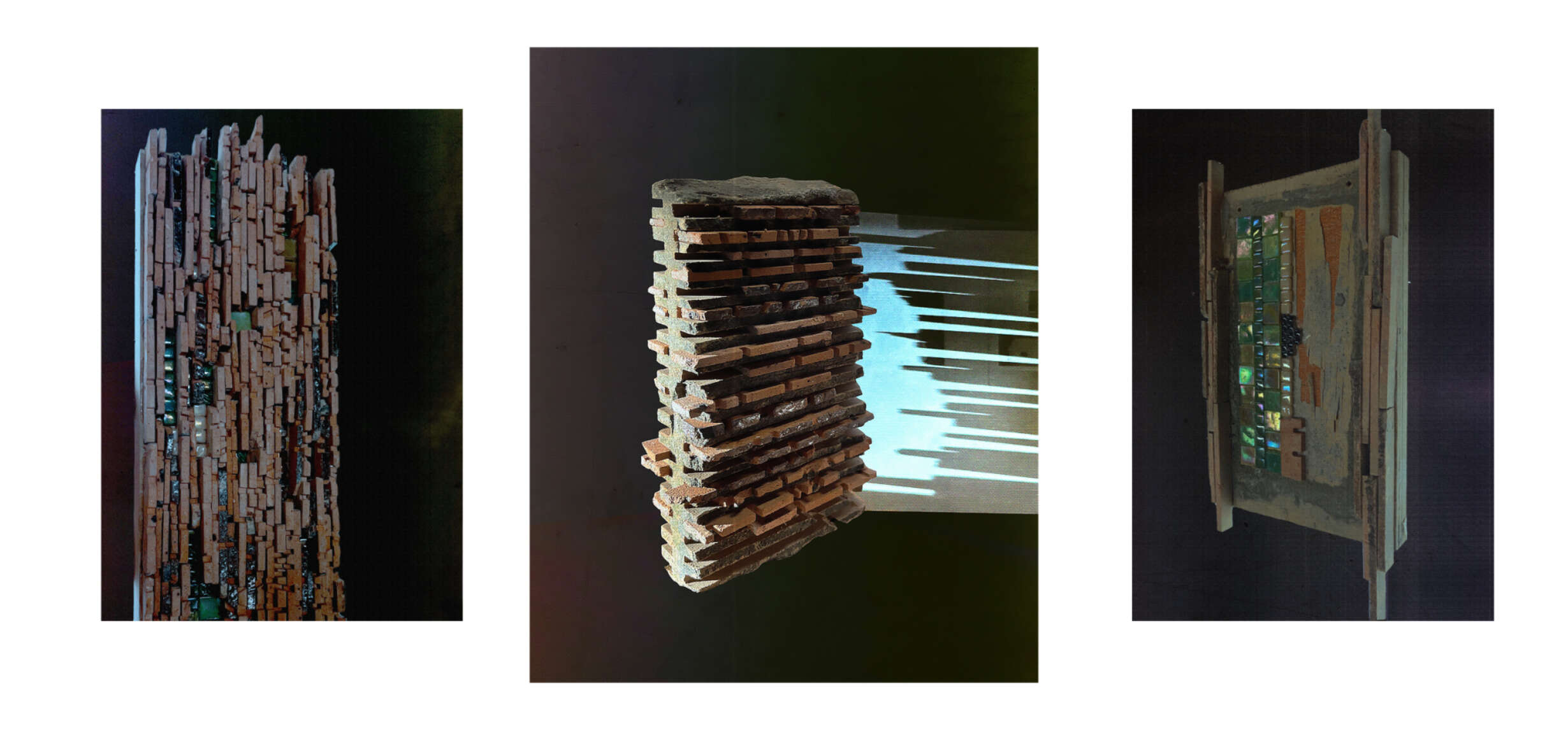
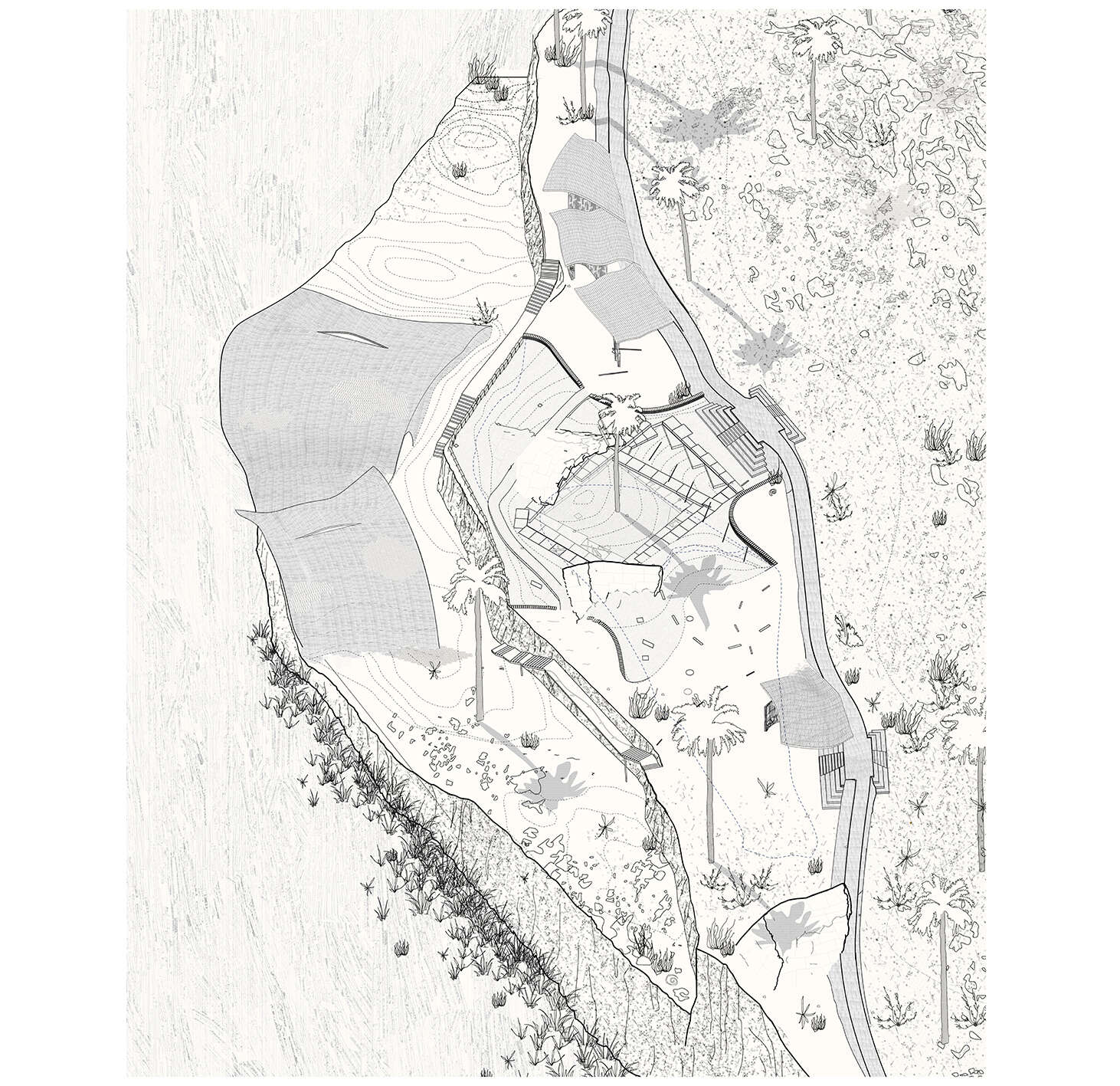
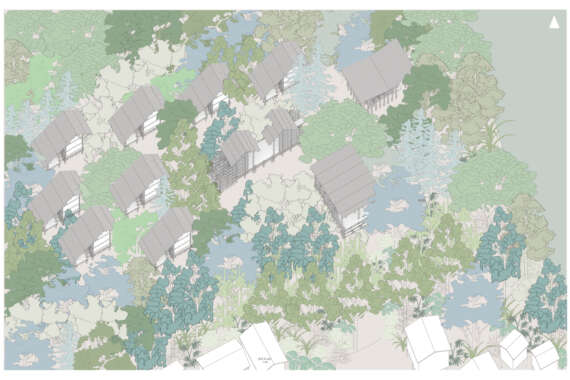
This thesis details a broad field of investigation in the aim of grounding a sense of loss caused by a disconnection to land. This connection is searched for through the making practice of mosaic, passed down to the author from her grandmother. The secondary grounding element comes in form of material: brick – which makes the physical connection between Aotearoa and Iraq. A sense of slowness is inherent to the making practice of mosaic, the time-consuming laying down of pieces and forming of fluid shapes and gradients, is mirrored in the build-up of time and history we see on the banks of a river. In this way, a clear connection is drawn between the methodology and site – an oasis on the Bank of the Tigris. What results from this investigation into the build-up of time within the stratified layers of earth, is an architecture which seeks to distort the scale of a mosaic and employ its conventions to form a fluid, undulating landscape which is rife with points of intrigue and pleasure.