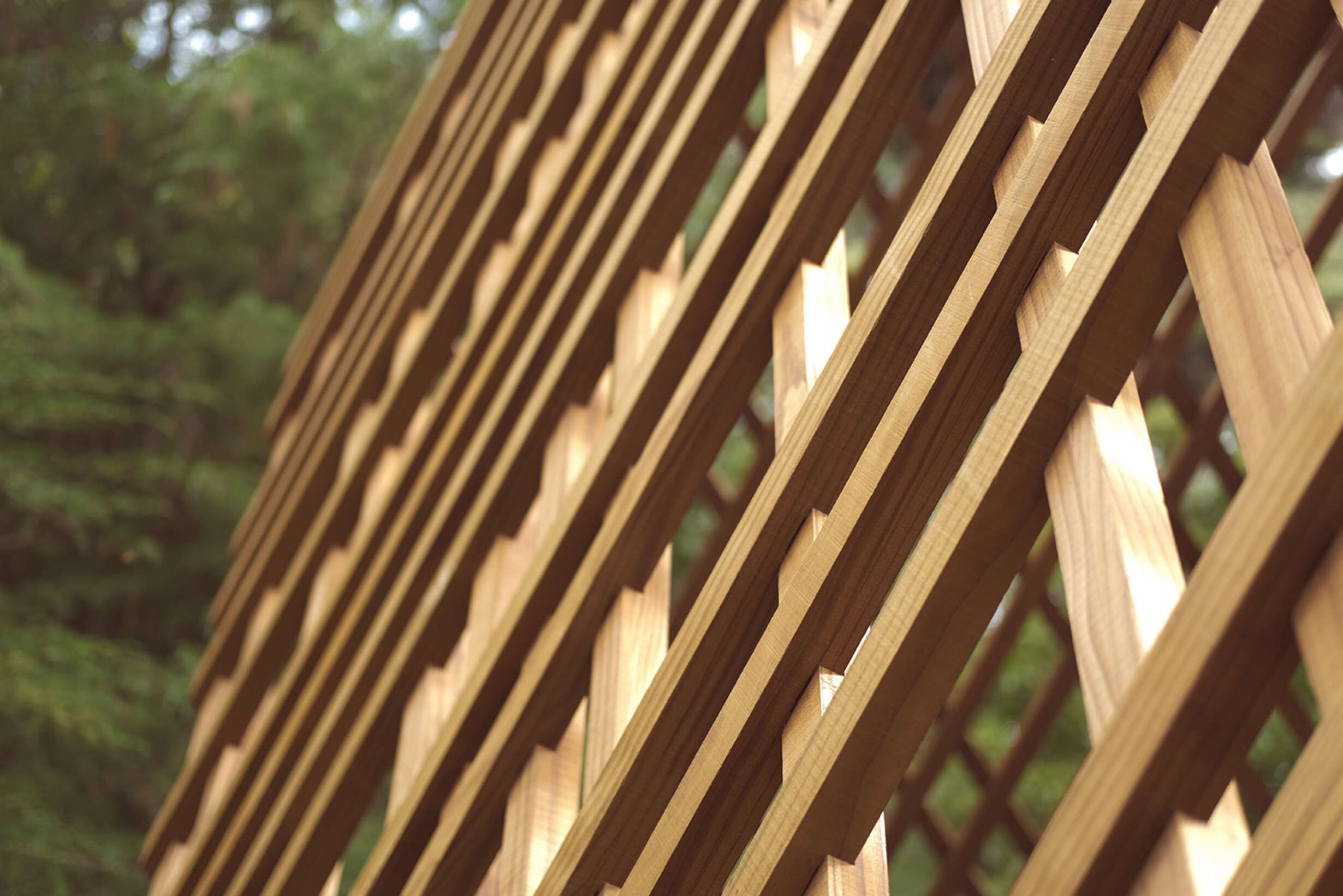
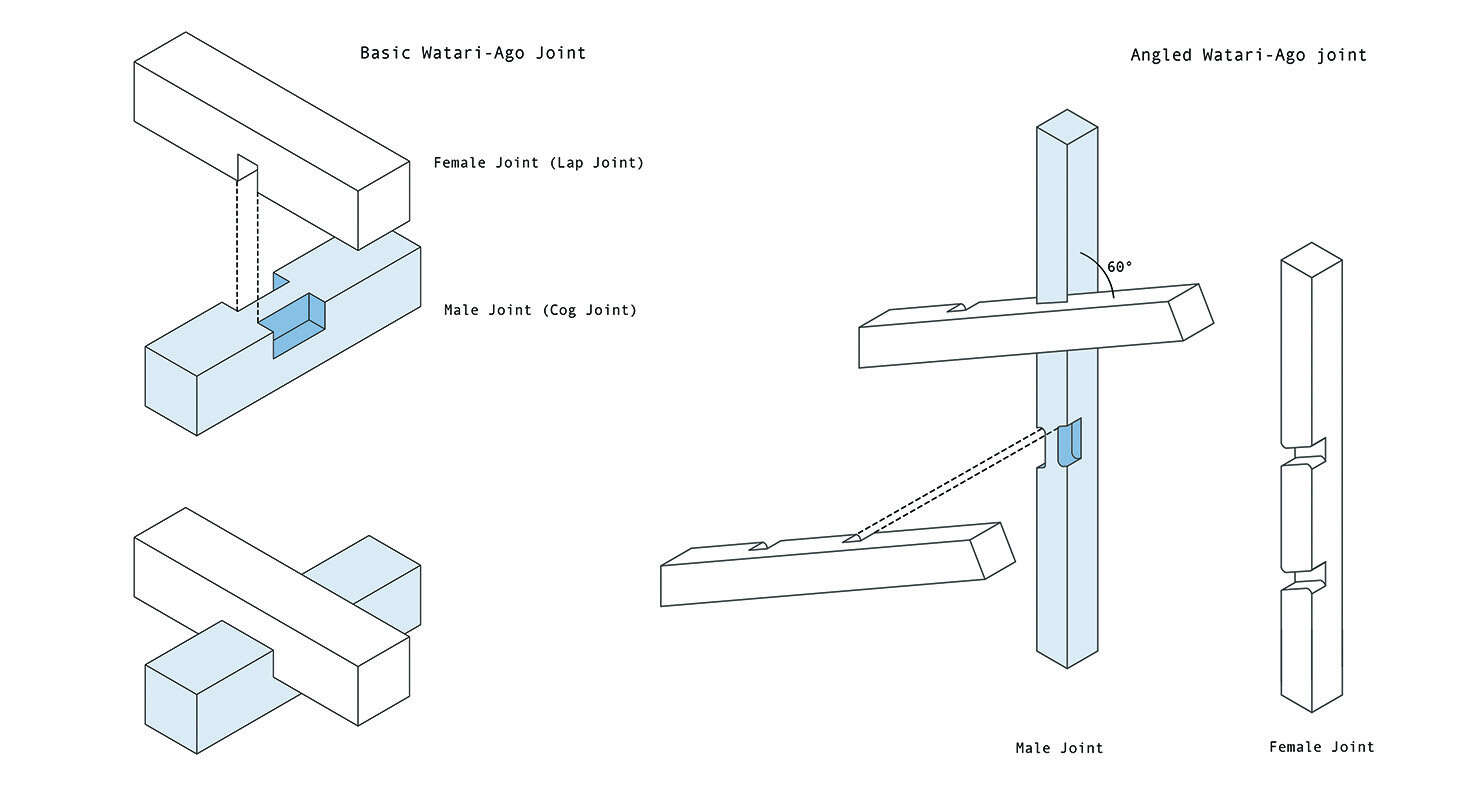
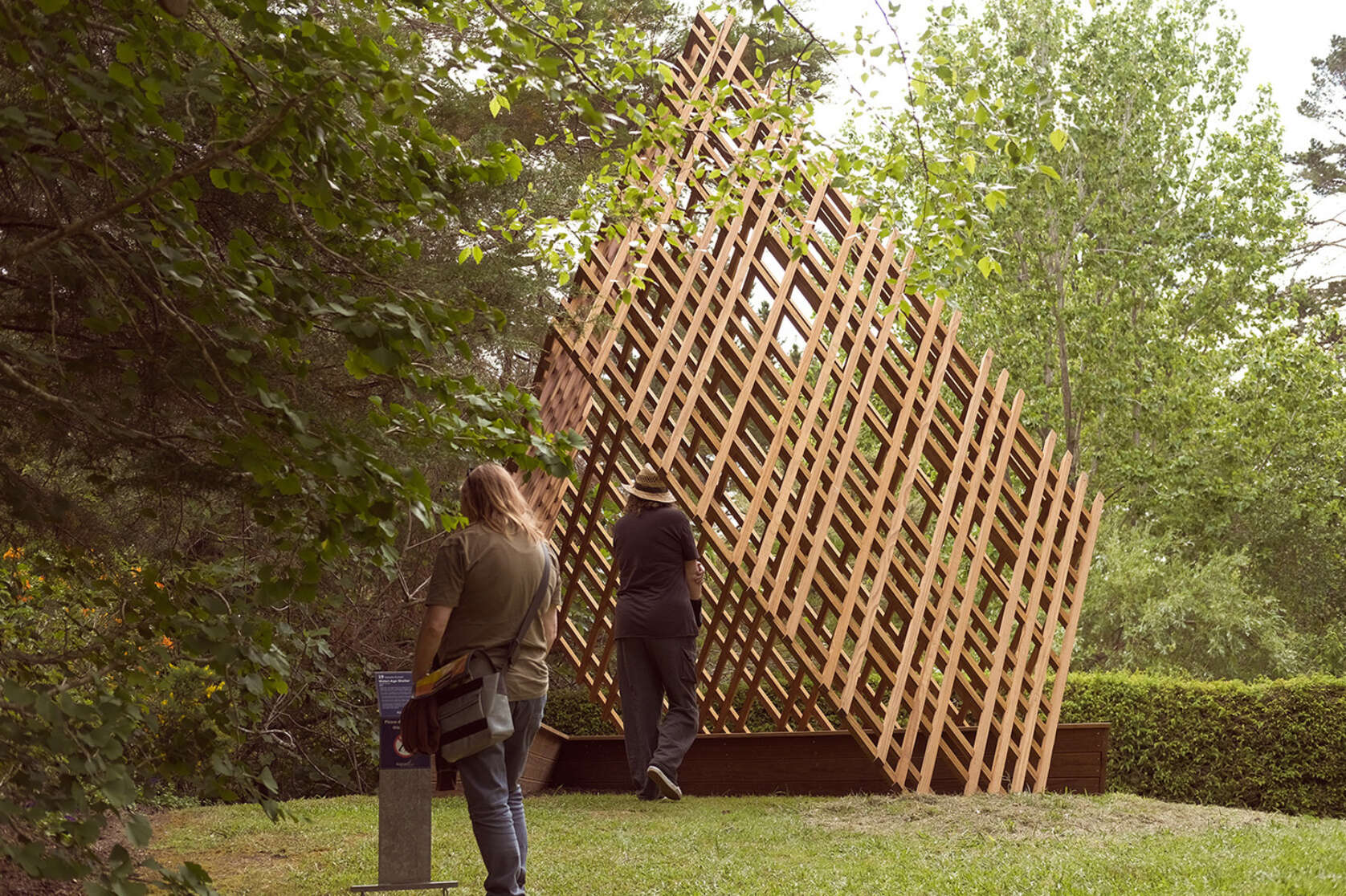
Watari-ago Shelter: Modernising Traditional Japanese Timber Joinery in the Contemporary Timber Architecture Scheme

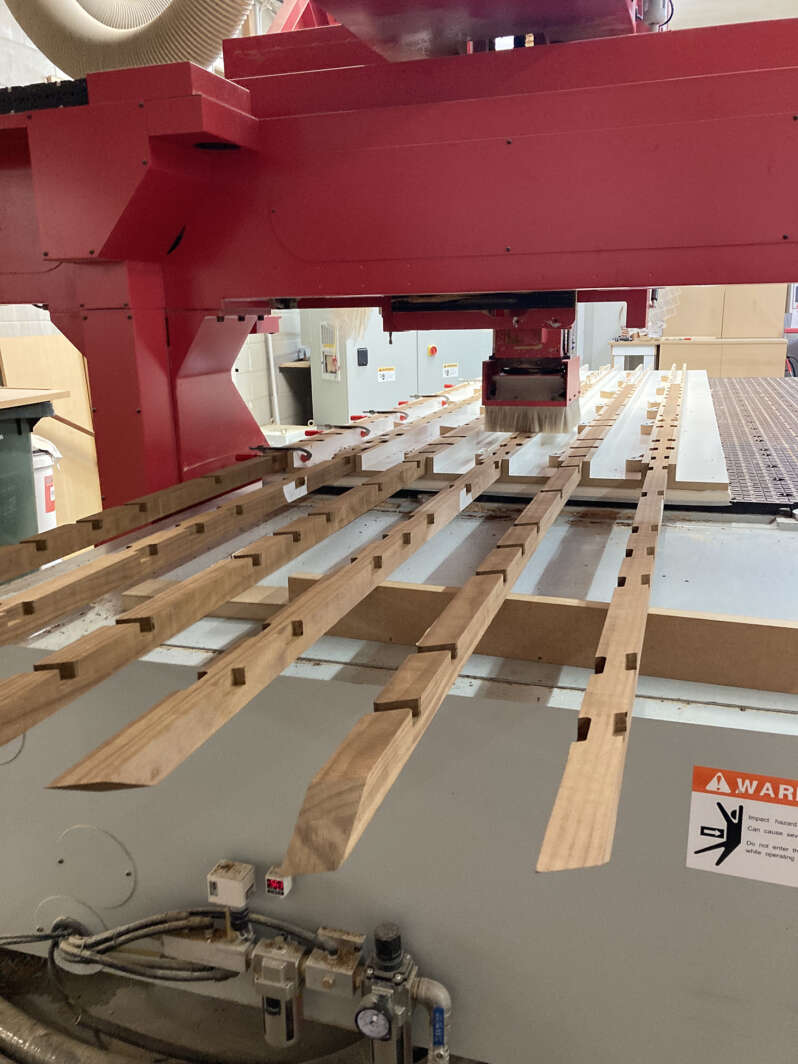
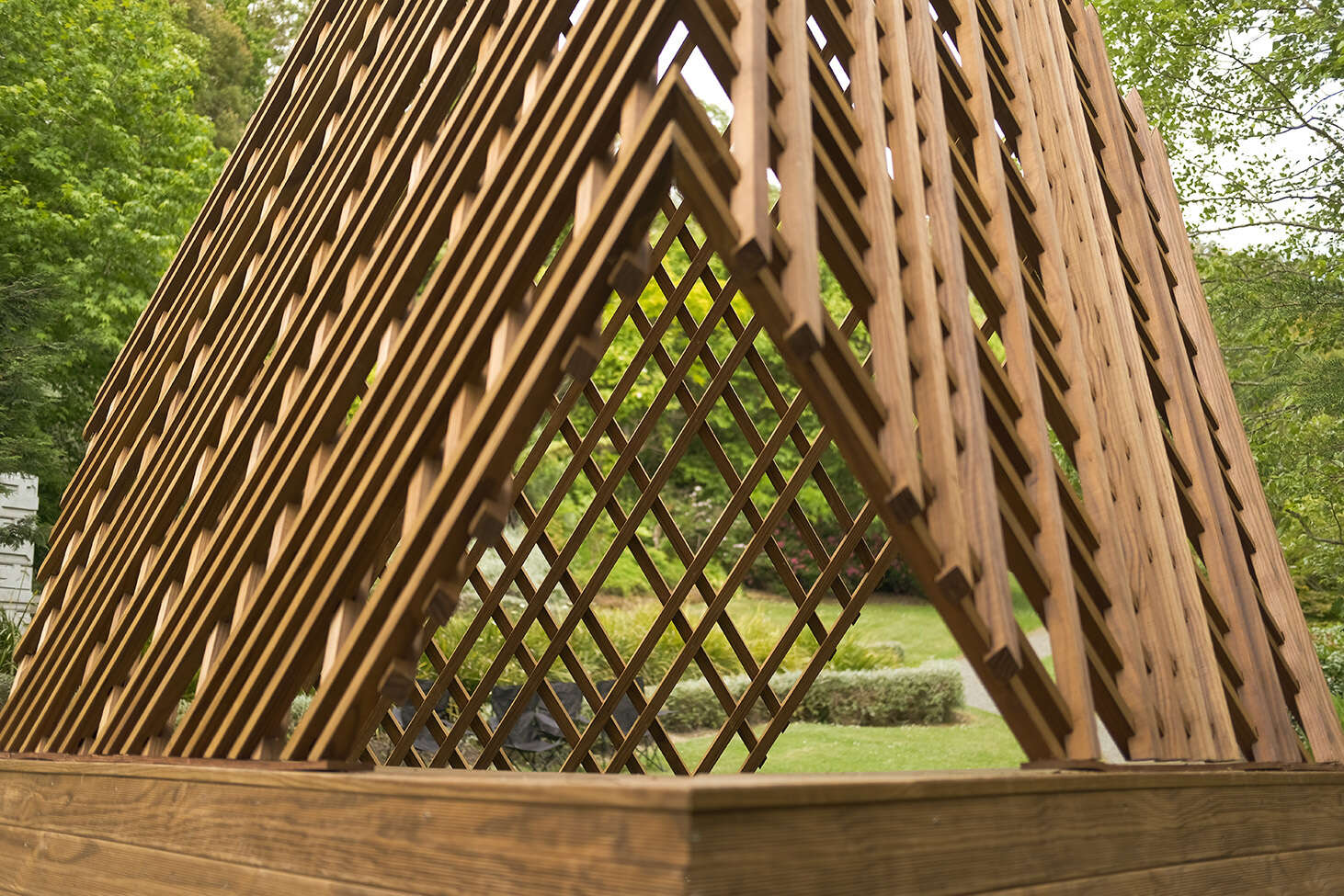
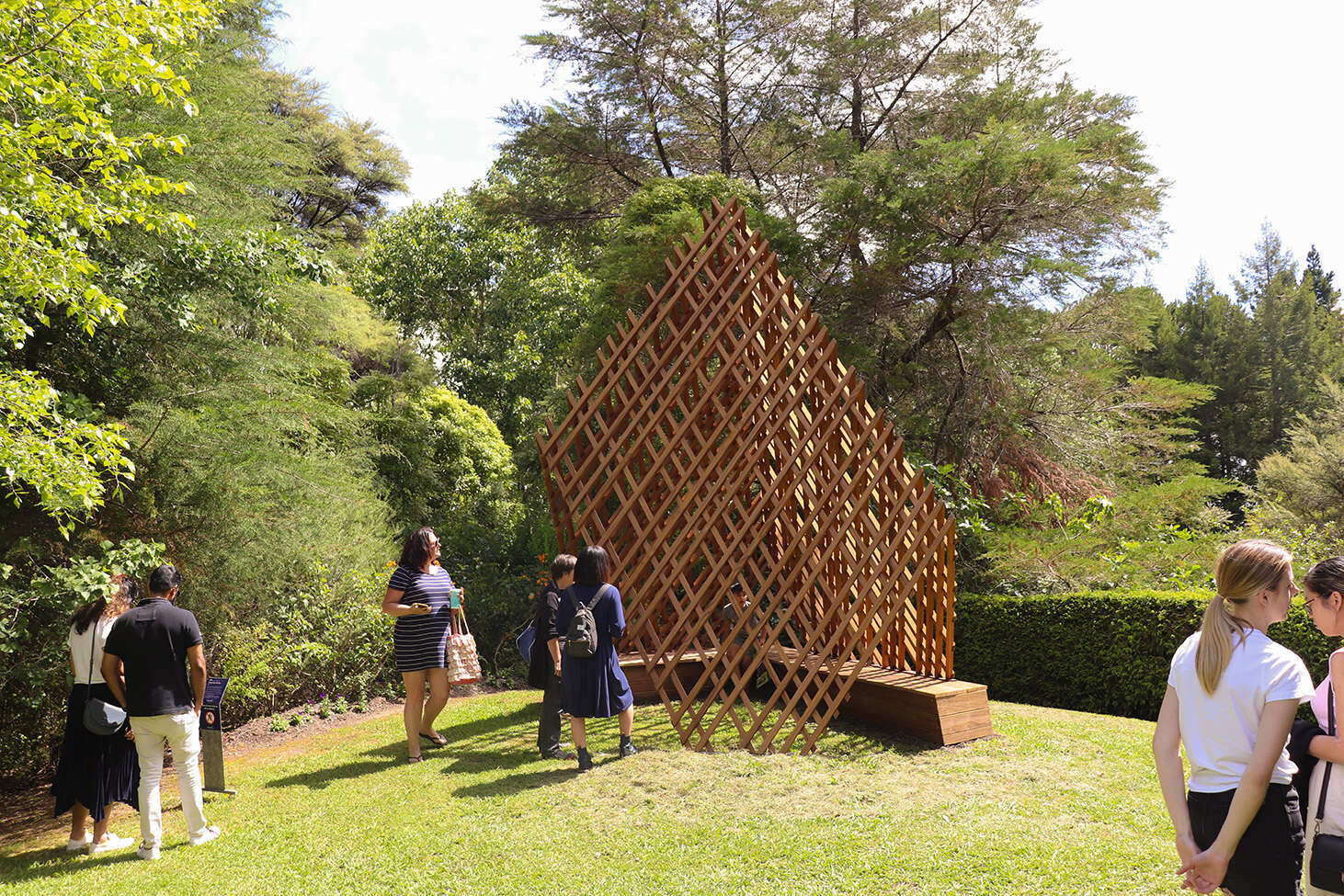
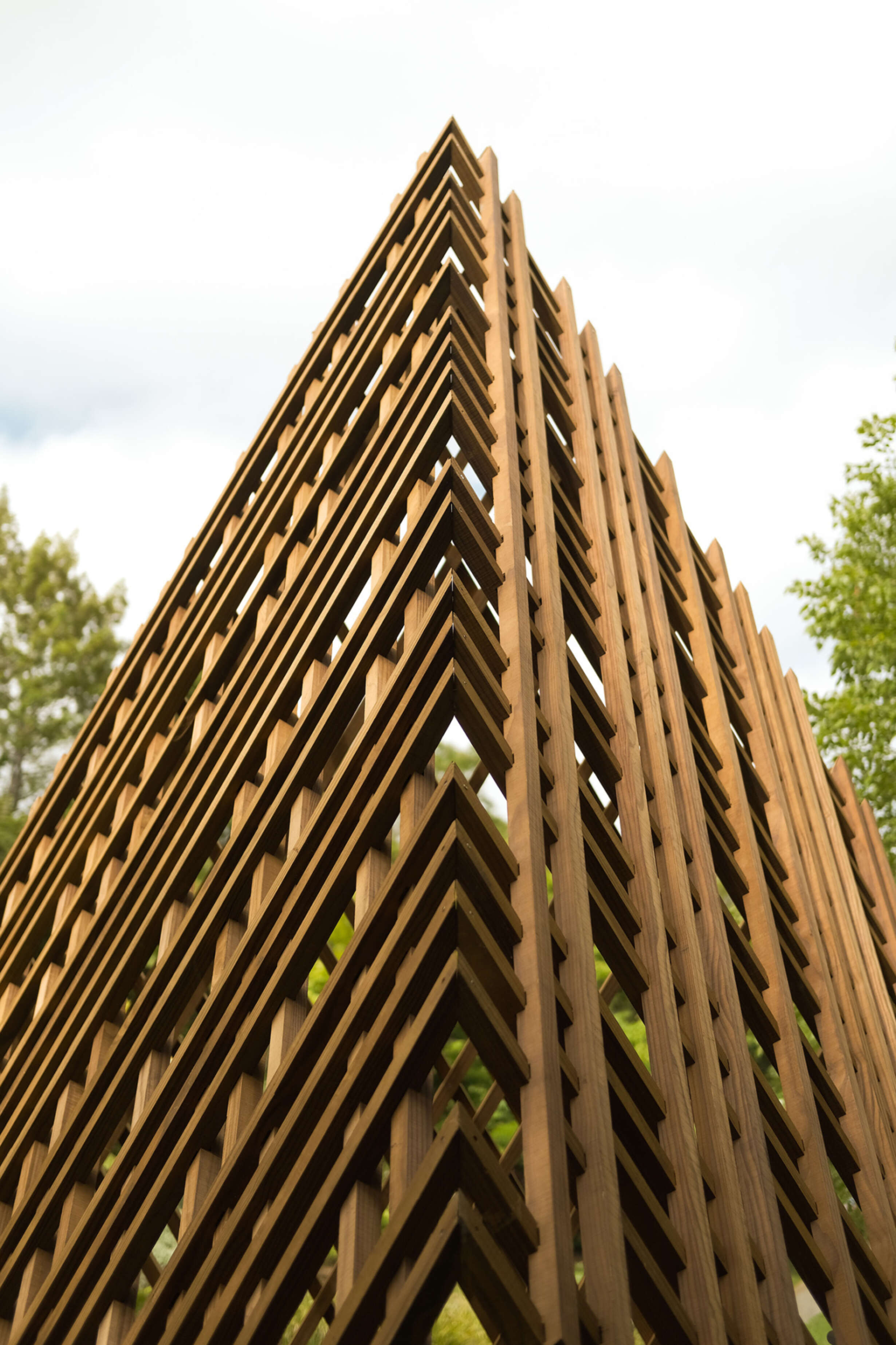
In architecture, timber is one of the oldest mediums used for construction and has been developed extensively through modern architecture schemes. However, in the digital aspect of timber design, highly specialised machines have been developed to mill large timber, while simple milling machines have not advanced past cutting sheet materials or smaller scale detailed designs.
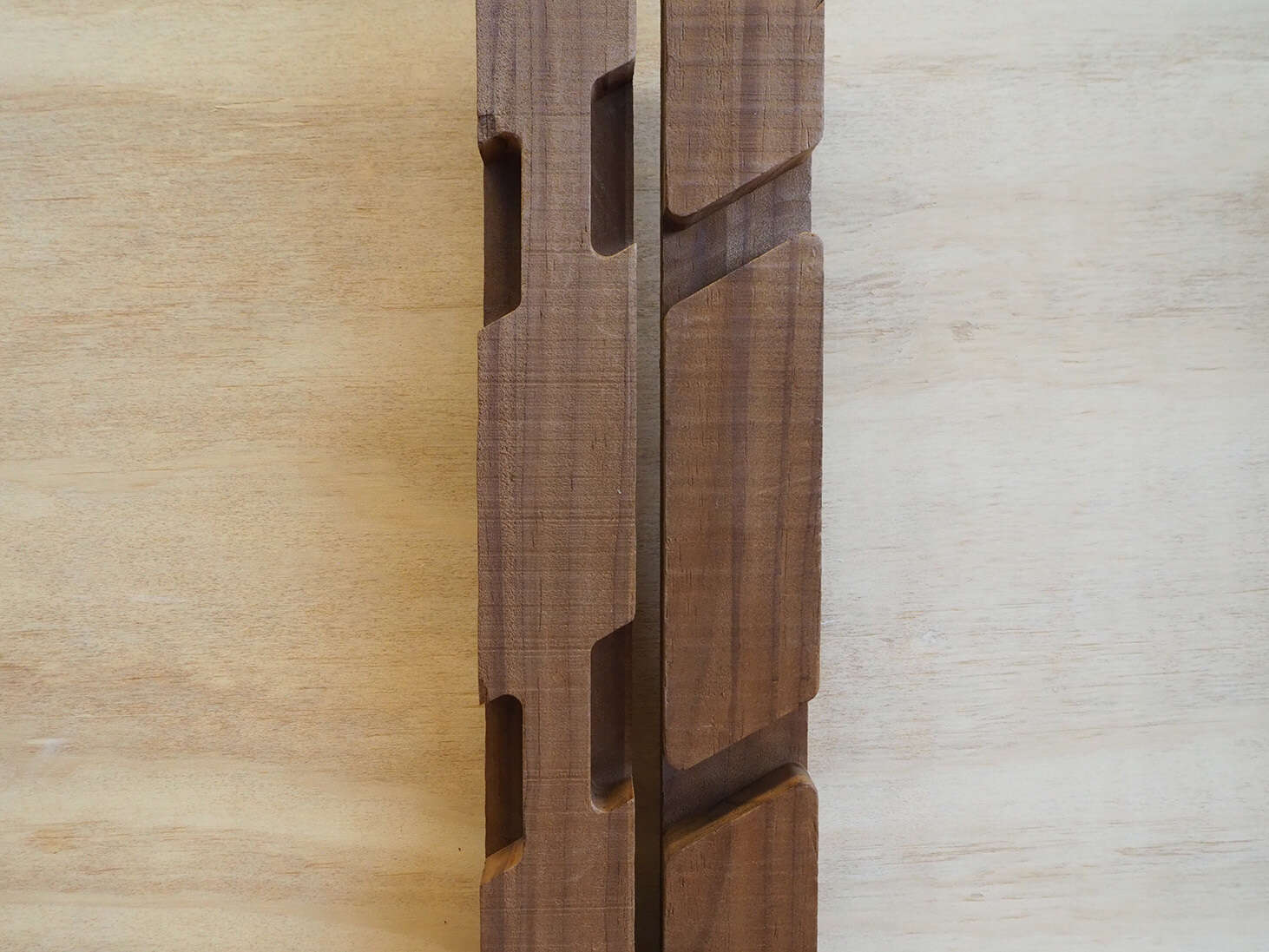
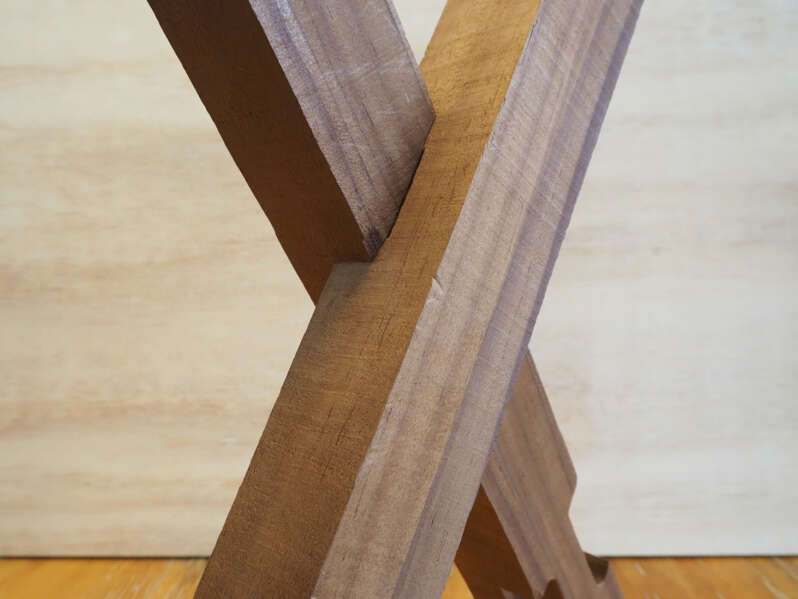
This thesis challenges the crevice between the small scale digital fabrication tools and timber architecture by using a simple three-axis CNC machine to achieve a sophisticated solid timber joint that would otherwise require an expensive and time-consuming procedure.